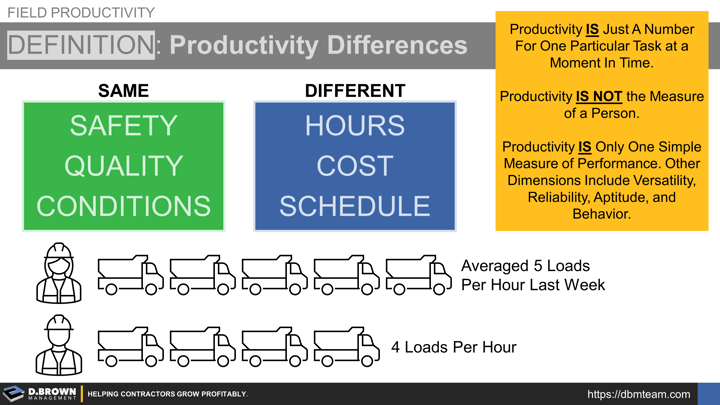
Productivity differences at the individual or equipment level mean that you have differences in hours, cost, or schedule given the same safety, quality, and conditions.
For example, if driver A averaged five loads per hour last week and driver B averaged four loads per hour then you could say there is a difference in their individual productivity if...
- Same trucks being used
- Same haul roads and route
- Same operating loading them
- Same unloading
- Same times of day or night
- Same safety (no speeding)
This is the first thing - making sure you are not confusing individual productivity differences with other factors that may have a material impact on absolute productivity. This is often difficult because our management systems typically tracking overall productivity, so it requires going out to the field to observe the work and understand what is behind those productivity numbers.
Remember:
- Productivity is just a number for one particular task at a moment in time.
- Productivity IS NOT the measure of a person.
- Productivity is only one simple measure of performance. Other dimensions include versatility, reliability, aptitude, and behavior.