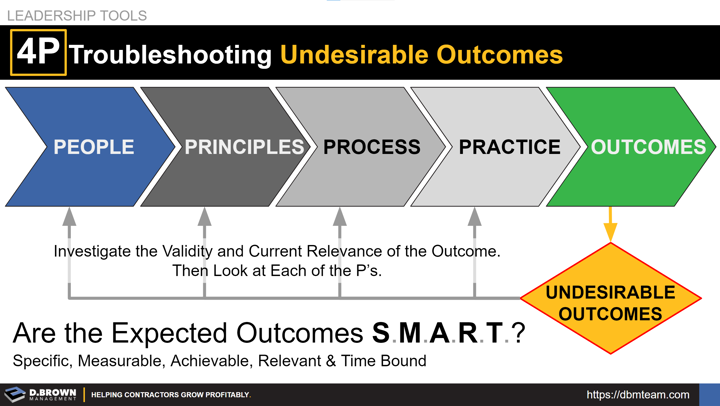
Question first whether the Expected Outcomes qualify as S.M.A.R.T. and especially if they are still the most relevant at this point in your growth cycle.
- People: Do you have the right people and does the organizational structure, including leadership development and succession preparation, support your business strategy, ensuring each person is working in their highest and best use?
- Principles: “As to methods, there may be a million and then some, but principles are few. The man who grasps principles can successfully select his own methods. The man who tries methods, ignoring principles, is sure to have trouble.” - Harrington Emerson
- Process: Do the processes, tools, and training support the strategies and principles, while leading toward the expected outcomes with minimal waste? Will they yield consistent outcomes without over-burdening the team?
- Practice: Are the processes, including each step and hand-offs, practiced deliberately with feedback for each cycle to ensure consistent outcomes?
As you are troubleshooting, ask yourself constantly whether the problem is about knowing or doing, while reconciling and aligning what is in your control.